
Note:
(i) All questions are compulsory. The marks allotted for each question are indicated against each question.
(ii) Write your name enrolment number, AI name, and subject on the top of the first page of the answer sheet.
1. Answer any one of the following questions in about 40-60 words.
a) Why do plants not need an Oxygen carrier like the humans in whom Oxygen is carried by Hemoglobin?
Answer: Plants don’t need an oxygen carrier like hemoglobin because they have a fundamentally different way of obtaining oxygen. They primarily use a process called photosynthesis, where they take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen as a byproduct. In photosynthesis, oxygen is produced directly from water molecules, and it’s released into the atmosphere.
In contrast, animals, including humans, rely on hemoglobin to transport oxygen through their bloodstream because they don’t produce oxygen themselves like plants do. This distinction in oxygen acquisition is a key difference between plants and animals.
b) Why does it happen that during hot summer months although you drink lot of water or cold drinks, you do not urinate much? Explain.
Answer: During hot summer months, you might feel thirsty and drink more water or cold drinks. However, excessive sweating in hot weather results in the body losing fluids through perspiration. This fluid loss is often greater than what you consume, which can lead to reduced urine production.
The body prioritizes cooling down through sweat over urinary excretion, resulting in less frequent urination. It’s essential to stay hydrated even if you don’t urinate as often in hot weather to prevent dehydration.
2. Answer any one of the following questions in about 40-60 words.
a) Conservation and Management of water has become an urgent step to be taken up by mankind. Write any four methods of such conservation steps.
Answer: The conservation and management of water are crucial due to increasing water scarcity. Four effective methods to address this issue are:
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater in tanks or underground reservoirs to replenish groundwater.
- Water Recycling: Treating wastewater for reuse in agriculture, industry, and even potable water.
- Reducing Water Waste: Fixing leaks, using efficient appliances, and being mindful of water consumption.
- Afforestation: Planting trees and vegetation to conserve soil and reduce water runoff.
Implementing these methods is essential to ensure sustainable water resources for future generations.
b) Which of the following fossils is a connecting link between reptiles and Birds? Briefly explain.
i) Eohippus,
ii) Archaeopteryx
Answer: Archaeopteryx is the connecting link between reptiles and birds. It lived around 150 million years ago and had features of both groups. It had reptilian characteristics like teeth and a long tail, while also having bird-like feathers and wings. This transitional fossil provides evidence for the evolution of birds from reptilian ancestors, supporting the theory of evolution and the relatedness of species.
3. Answer any one of the following questions in about 40-60 words.
a) Which of the following is found in plant cells only? Mitochondria, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Cell wall and Ribosome
Answer: Cell wall is found in plant cells only.
- Mitochondria: Present in both plant and animal cells, involved in energy production.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: Present in both, aids in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Ribosome: Present in both, involved in protein synthesis.
- Cell wall: A rigid structure found only in plant cells, providing support and protection.
The presence of a cell wall is a key feature distinguishing plant cells from animal cells.
b) Outline the diagram of the kidney and briefly describe where ultra filtration occurs in the kidney and which molecules pass during ultra filtration.
Answer:

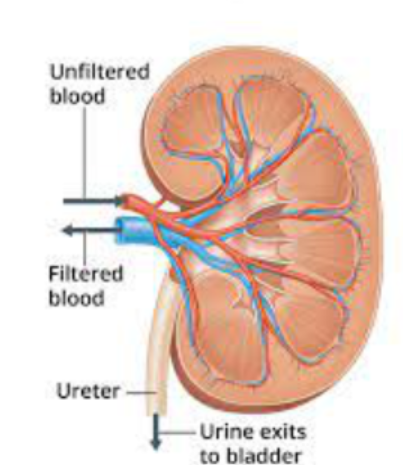
Kidney Diagram:
- Kidneys are bean-shaped organs in the abdominal region.
- Each kidney has an outer cortex and inner medulla.
- Blood vessels enter and exit at the renal hilum.
Ultrafiltration in the Kidney:
- Ultrafiltration occurs in the renal corpuscle (glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule).
- During ultrafiltration, small molecules like water, glucose, salts, and waste products are filtered from the blood into the renal tubules.
- Large molecules like proteins and blood cells are retained in the blood.
4. Answer any one of the following questions in about 100-150 words.
a) The teacher said frog is an ectotherm what did she mean? How does frog then survive in the extremely cold seasons?
Answer: The teacher meant that a frog is an ectotherm, which is an organism that relies on external sources to regulate its body temperature.
How Frogs Survive in Cold Seasons:
- Burrowing: Frogs burrow into the ground or mud, where temperatures are more stable and not as cold as the surface.
- Hibernation: They enter a state of hibernation, where their metabolic rate drops significantly, reducing their energy needs and allowing them to survive on stored resources.
- Aquatic Habitats: Some frogs survive in the water where temperatures are milder, often staying in a semi-dormant state.
- Anti-freeze Proteins: Some frogs produce antifreeze proteins that prevent ice crystal formation in their tissues.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Frogs are highly adaptable and can adjust their behavior to cope with temperature changes. They may bask in the sun to warm up or seek shade to cool down.
Frogs have evolved various strategies to cope with cold seasons while being ectothermic, allowing them to endure extreme cold conditions.
b) Because of a blockage in the bile duct of a person, his small intestine was not getting a digestive juice in sufficient amount. His doctor advised him to avoid fatty food. Name the digestive juice in question and state how the juice helps in the digestive process.
Answer: The digestive juice in question is bile, which is produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile plays a crucial role in the digestive process by emulsifying fats. Here’s how it helps:
- Emulsification: Bile contains bile salts that break down large fat globules into smaller, more manageable droplets. This process is called emulsification, which increases the surface area of fats, making it easier for enzymes to access and digest them.
- Fat Digestion: Bile enables lipase, an enzyme produced by the pancreas and small intestine, to effectively break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. This step is essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients in the small intestine.
- Absorption: Once emulsified and digested, fats are absorbed in the small intestine. Bile also aids in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
In the absence of sufficient bile, fat digestion and absorption are compromised, leading to malabsorption of essential nutrients and the potential development of gastrointestinal issues. The doctor’s advice to avoid fatty foods helps reduce the workload on the compromised digestive system and minimizes discomfort for the individual.
5. Answer any one of the following questions in about 100-150 words.
a) A person has more than normal sugar in blood. He/She excretes a large amount of urine loaded with sugar. What is this due to ? Explain ?
Answer: This condition is due to diabetes mellitus, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. There are two main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This results from the immune system mistakenly attacking and destroying insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Without insulin, blood sugar cannot enter cells, leading to high sugar levels in the bloodstream. Excess sugar is then excreted in the urine.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. The sugar remains in the blood, and the kidneys work harder to filter it, causing sugar to be lost in the urine.
High blood sugar can lead to various health complications, so diabetes management, including medication, diet, and exercise, is crucial for those affected.
b) Some plants in one corner of your kitchen garden are showing poor growth and their leaves are becoming yellow. This could be due to the deficiency of some essential element. Name the essential element whose deficiency is causing this problem and mention why the leaves are turning yellow. Also discuss how are the minerals absorbed by the plants?
Answer: The essential element whose deficiency is likely causing this problem is iron. When plants lack iron, they develop a condition known as “iron chlorosis,” which manifests as yellowing leaves due to a lack of chlorophyll production. Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis, and when it’s insufficient, the leaves lose their green color.
Mineral Absorption in Plants: Plants absorb minerals primarily through their roots. The process involves:
- Root Hairs: These tiny, hair-like structures on the roots provide a large surface area for absorption.
- Active Transport: Minerals are absorbed against the concentration gradient through active transport, which requires energy.
- Mycorrhizal Symbiosis: Some plants form mutualistic associations with mycorrhizal fungi that enhance mineral absorption.
- Nutrient Solution: Minerals are absorbed in the form of ions dissolved in water from the soil solution.
- Translocation: Once absorbed, minerals are transported through the plant via the xylem to reach various tissues for growth and function.
Correcting iron deficiency often involves supplementing the soil with iron-based fertilizers or adjusting soil pH to improve iron availability for plants.
6. Prepare any one project out of the given below:
a) Visit to the zoo / sanctuary / biosphere reserve / aquarium / bird sanctuary / Biodiversity Park
Collect your friends make a group and organize a trip to one of the above mentioned places. Carry a camera or mobile to take photographs. You have already learnt how important ‘biodiversity’ is for humans. Our plants and animals are also the country’s heritage. Once you get familiar, you shall enjoy knowing more about their behaviour, adaptations and life cycles.
Take a notebook and note down names of the animals you have seen. Use the internet to know their scientific names and make an album of the pictures of animals you have become familiar with. Observe their behaviour and you may now prepare
1. A power point presentation
2. Story book describing their behavior
3. Photographic album
4. Scrapbook or
5. A report on the trip
Answer: Trip Itinerary:
- Preparation:
- Gather your friends and organize a group trip to one of the mentioned places.
- Equip yourself with a camera or mobile to capture the beauty of nature.
- Exploration:
- Focus on understanding the importance of biodiversity for humans and appreciate the country’s rich heritage in terms of plants and animals.
- Take a notebook to jot down the names of the animals you encounter.
- Documentation:
- Use the internet to research and find the scientific names of the animals you observed.
- Create an album of the pictures you capture, organizing them by species.
- Creation Phase:
- Power Point Presentation:
- Compile information on the importance of biodiversity.
- Highlight the observed behaviors, adaptations, and life cycles of the animals.
- Story Book:
- Craft a narrative describing the behavior of the animals, their interactions, and the unique features you observed.
- Photographic Album:
- Create a visually appealing album with captions for each species, including both common and scientific names.
- Scrapbook:
- Blend photographs with personal reflections, notes, and interesting facts about the animals.
- Report:
- Summarize the trip, discussing the significance of biodiversity and its conservation.
- Include key findings, interesting anecdotes, and recommendations for future visits.
- Power Point Presentation:
Post-Trip Activities:
- Share your experiences and creations with your friends and classmates.
- Consider presenting your Power Point presentation to your school or community to raise awareness about biodiversity.
Remember to approach this trip with curiosity and a desire to learn. Nature has a lot to offer, and your documentation will not only serve as a personal memento but also as a tool to inspire others to appreciate and conserve our precious biodiversity.
(b) Constructing a greenhouse from scrap material
You are learning a lot about the ‘greenhouse effect’ and global warming. Why not see for yourself how sun rays heat the greenhouse and keep it warm enough for plants to survive in it. You shall need some pieces of glass for transparent plastic sheets, Brown cello tape, cardboard, plastic pipes to circulate water inside the chamber, toy fan to cool the inside.
Assemble all the parts and build the green house. Keep it in the Sun on different days. Note atmospheric temperature from the newspaper and use a thermometer to check the temperature inside the greenhouse that you have created.
Check the temperature from time to time and on different days of the month and prepare a comparative statement of the changes in temperature that you observed.
Embarking on a project to construct a greenhouse from scrap materials is a fantastic way to understand the greenhouse effect and its impact on temperature. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you with this exciting experiment:
Materials Needed:
- Pieces of glass or transparent plastic sheets
- Brown cello tape
- Cardboard
- Plastic pipes for water circulation
- Toy fan
- Thermometer
Construction Steps:
- Frame Assembly:
- Use cardboard to create a sturdy frame for the greenhouse. Ensure it has a sloping roof to maximize sunlight exposure.
- Covering:
- Attach the pieces of glass or transparent plastic sheets to the frame using brown cello tape. This will allow sunlight to penetrate and create the greenhouse effect.
- Ventilation System:
- Integrate plastic pipes into the structure for water circulation. This will help regulate the temperature inside the greenhouse.
- Cooling Mechanism:
- Place a toy fan inside the greenhouse. This will simulate the cooling effect and help you understand the role of ventilation in temperature control.
- Placement:
- Set up your greenhouse in a location with ample sunlight. Ensure it receives consistent sunlight on different days.
Experiment and Observation:
- Temperature Monitoring:
- Use a thermometer to measure the temperature inside the greenhouse regularly.
- Record the atmospheric temperature from the newspaper for comparison.
- Comparative Statement:
- Note the temperature variations inside the greenhouse on different days.
- Prepare a comparative statement highlighting changes in temperature over time.
- Data Collection:
- Document your observations in a notebook, including any patterns or trends you notice.
Analysis and Conclusion:
- Reflect on your findings and relate them to the greenhouse effect.
- Consider the implications for real-world scenarios and global warming.
